Blockchain is a buzzword that you might have heard a lot in recent years, but what exactly is it and why does it matter? In this blog post, we will try to answer these questions and give you a brief overview of the history and evolution of blockchain technology.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions in a secure, chronological, and immutable way. A ledger is a file that keeps track of all transactions that have ever occurred. A distributed ledger means that the ledger is not stored in a central location, but rather shared among multiple nodes (computers) in a network. A secure ledger means that the transactions are verified by cryptographic algorithms and protected from unauthorized changes. A chronological ledger means that the transactions are ordered by the time they occur. An immutable ledger means that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted.

A blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions and some other information, such as a timestamp and a reference to the previous block. Each block has a unique identifier called a hash, which is generated by applying a mathematical function to the block’s content. The hash serves as a digital fingerprint that ensures the integrity of the block and links it to the previous block. The first block in the chain is called the genesis block and has no reference to any previous block.
The nodes in the network communicate with each other to reach a consensus on the state of the ledger. This means that they agree on which transactions are valid and which are not, and which block should be added to the chain next. The consensus mechanism varies depending on the type of blockchain, but it usually involves some form of incentive or penalty for the nodes to behave honestly and follow the rules. For example, some blockchains use a proof-of-work system, where nodes have to solve complex mathematical puzzles to create new blocks and earn rewards. Other blockchains use a proof-of-stake system, where nodes have to stake some amount of their own tokens to participate in the consensus process and risk losing them if they act maliciously.
The main advantages of blockchain technology are:
- Decentralization: There is no central authority or intermediary that controls or validates the transactions. This reduces the risk of censorship, corruption, fraud, or manipulation.
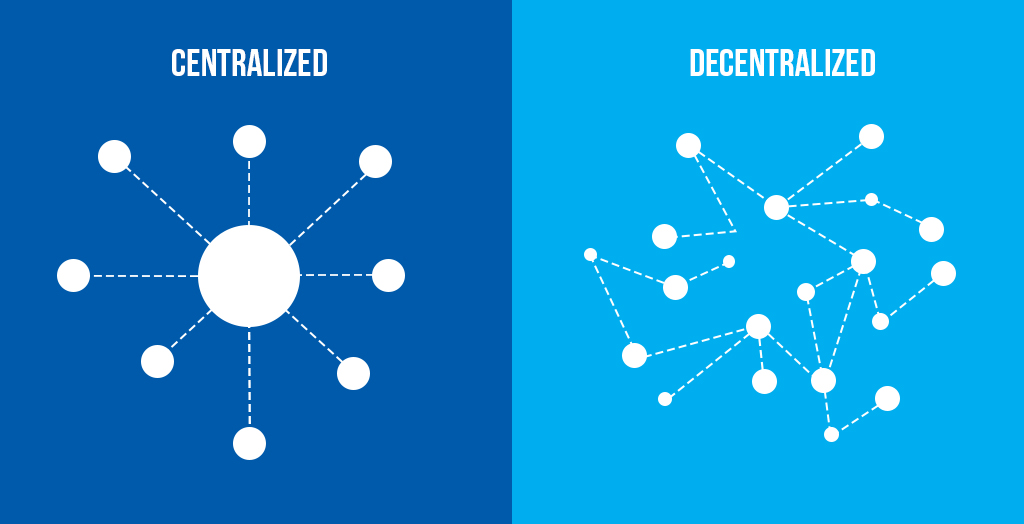
- Transparency: The transactions are visible to anyone who has access to the network. This increases trust and accountability among the participants.
- Security: The transactions are encrypted and verified by cryptographic algorithms. This makes it very difficult for anyone to tamper with or forge the transactions.
- Immutability: The transactions are permanently recorded and cannot be changed or erased. This creates an auditable and verifiable history of events.
History of Blockchain
The concept of blockchain can be traced back to 1991, when two researchers named Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta proposed a system for time-stamping digital documents in a way that they could not be tampered with 1. They used cryptographic techniques to link the documents in a chain of blocks, where each block contained a hash of the previous block. In 1992, they improved their system by incorporating Merkle trees, which allowed them to store multiple documents in one block 2.
However, their system was not widely adopted and remained unused until 2008, when an anonymous person or group using the name Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” 3. Nakamoto combined the idea of blockchain with a peer-to-peer network and a digital currency called bitcoin. Bitcoin was designed as a decentralized alternative to traditional money systems, where transactions are validated by network nodes without relying on any trusted third party. Bitcoin also introduced a novel consensus mechanism based on proof-of-work, where nodes compete to create new blocks and earn rewards in bitcoins.

Bitcoin was launched in January 2009 with the creation of the genesis block by Nakamoto 4. Since then, bitcoin has grown to become the most popular and valuable cryptocurrency in the world, with millions of users and transactions every day. Bitcoin also inspired many other cryptocurrencies and blockchain projects that have emerged over the years, such as Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple, Cardano, etc.
Evolution of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has evolved beyond its original application as a medium of exchange for cryptocurrencies. Today, blockchain is used for various purposes across different industries and sectors, such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, gaming, art, etc. Some of the current trends and developments in blockchain are:
- Smart contracts: These are self-executing agreements that are encoded on the blockchain and triggered by predefined conditions. Smart contracts enable automated and transparent transactions without intermediaries or human intervention. For example, smart contracts can be used for escrow services, in surance claims, voting systems, etc.

- Decentralized applications (DApps): These are applications that run on a distributed network of nodes using blockchain as their backend infrastructure. DApps can offer various services and functionalities to users, such as social media, e-commerce, gaming, etc. For example, DApps can be used for peer-to-peer lending, decentralized exchanges, online gambling, etc.

- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs): These are unique and indivisible digital assets that are minted and traded on the blockchain. NFTs can represent anything of value or significance, such as art, music, collectibles, etc. For example, NFTs can be used for digital ownership, authentication, provenance, etc.

- Decentralized finance (DeFi): This is a movement that aims to create an open and accessible financial system that operates on the blockchain without intermediaries or regulations. DeFi offers various financial services and products to users, such as lending, borrowing, trading, investing, etc. For example, DeFi can be used for yield farming, liquidity mining, stablecoins, etc.

Conclusion
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to transform the way we exchange value and information in the digital world. Blockchain offers many benefits such as decentralization, transparency, security, and immutability. Blockchain also enables new possibilities and opportunities for innovation and creativity across various domains and applications.
I hope you found this post useful and informative. If you have any questions or any feedback, feel free to leave a comment below.
Stick to this series as you'll learn a lot :)

